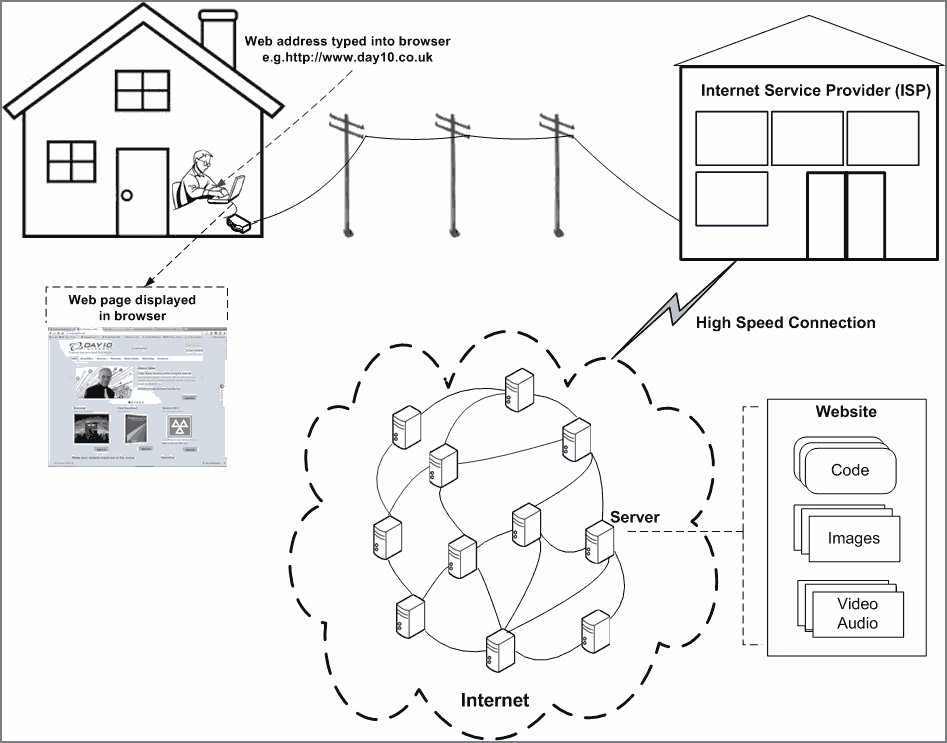
In this article I’m going to explain what a website is and how it works. The article is aimed at people who view websites but have little or no understanding of what happens behind the scenes. So I make no apologies for the fact that I explain the terms and processes involved in very simple terms.
Take a look at the following picture which illustrates the what happens when we sit down in front of our computer screens to view a website.
To explain what happens let’s go through the process step by step as follows. You can refer to the definitions at the end of the article for further explanation as you read through the steps.
- In order to display a web page on your computer you, first of all need to load your web browser.
-
To do that, type in the address of the website or webpage that you want to display – e.g. http://www.example.co.uk – and press the enter button.
-
The address just typed is sent to your router, then down the telephone line to your ISP (Internet Service Provider) from where it is sent, via a high speed connection, to a web server connected into the Internet.
-
When the web server receives the request for the web page it responds by sending back some HTML code.
-
The HTML code is routed back to your computer, through the high speed connection, via your ISP, telephone line, and router. The HTML code contains text to display on the web page, the addresses of any images, videos or sound files that are to be included in the web page, and instructions for displaying it all.
-
Next the browser sends these addresses contained in the HTML code back to the server which then responds by sending the relevant images, videos and sound files back to your computer.
-
After receiving them, your browser then puts them together with the text it previously received and displays the web page.
-
The entire process, after you have typed the address and pressed the Enter button, happens in a fraction of a second.
-
Instead of typing the address, as in step 2, the same process occurs when you click a link, for example a link in search results or a link on a web page. The link merely sends an address to the server.
In simple terms, that’s all there is to it.
Now let’s look at some explanations of the things mention in this process.
Web Browser – a computer program for displaying web pages on a computer screen. Examples of web browsers are – Microsoft Internet Explorer, Google Chrome (not to be confused with Google Search), Firefox, Opera, Safari.
ISP – Internet service Provider – an organization that provides access to the Internet. An ISP typically provides you with a Broadband service on a standard telephone line and then connects to the Internet via a very high speed connection.
Internet – a global system of millions of interconnected computers.
Wold Wide Web (or Web) – A system of Internet servers that support specially formatted documents. The documents are formatted in HTML.
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) – a markup language that supports links to other documents, as well as graphics, audio, and video files.
Web Server – A computer containing specific software that responds to requests across the Internet to provide web pages in the form of HTML code.
Website – a set of related web pages (HTML Code, images, video, sound) hosted on a web server and accessible via a network such as the Internet
In future articles I will explain some other common functions that we all use as part of our everyday Internet usage. For example:
- Search Engines
- Online Shopping
- Internet Marketing
- and much more
In the meantime if you have any comments of questions, please click the Read More link below and type in the box provided.